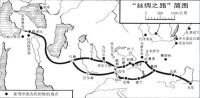
The Silk Road
The Silk Road (丝绸之路) was an ancient commercial route, which wriggled through mountains, lakes and deserts, from China to southern Europe.
The road starts at China’s ancient capital of Chang’an (today’s Xi’an in Shaanxi Province), travelling through the Hexi (Gansu) Corridor, Jade Gate Pass, Yang Pass, Xinjiang, Pamir high plateau, Central Asia, and Western Asia, eventually leading to Europe.
The name "Silk Road" was adopted in the 1970s by German geologist Ferdinand Freiherr von Richthofen for its original use in transporting China’s silks.
The road was paved by the Chinese historic figure Zhang Qian (张骞), who set off for the first time from Chang’an to Xiyu (西域) as an envoy with Emperor Han Wudi (汉武帝)’s order to ally with the western regions in dealing with the challenge of Xiongnu (匈奴), a nomadic group involved in several wars with Zhongyuan (中原), the territory of Emperor Wudi in the Western Han Dynasty (206 BC-24 AD).
Unfortunately, the envoy delegate was discovered by the Xiongnu, and Zhang was held hostage for 11 years before he escaped. He subsequently went back to Chang’an and reported his experience to Emperor Wudi. According to Zhang, people in the western region were no longer willing to fight against Xiongnu, instead, peaceful commercial exchanges became the mainstream.
In hearing Zhang’s proposal, the Emperor Wudi sent him a second time in 119 AD to Xiyu to establish peaceful relations between the Western Han and the kingdoms in Xiyu. Thus mutual commercial exchanges began between the Chinese and Central Asian peoples.
In 60 AD, the kingdoms in Xiyu began to subordinate to the Eastern Han, which then set up an administration—Xiyu Duhu (西域都护) to take charge of the region. Thus began the era of Xinjiang (basically the territory of Xiyu) composing an integral part of China.
In 73 AD, Ban Chao (班超), another early Chinese diplomat, assumed the role of administrator of Xiyu Duhu and assisted the kingdoms there to oust Xiongnu control of the area. He also sent his envoy Gan Ying (甘英) via the Persian Gulf to the area, approximately the size of today’s Rome, to enhance the commercial and cultural exchanges along the road.
For thousands of years, the road, which formerly carried countless numbers of caravans, fell into silence with the rise of European navigation and China’s gradual isolationism.
Yet, today, the Silk Road has been revitalized due to a reminiscent public which has expressed immense interest in the historic significance of the route and its role in enhancing the relations between China and Central Asian and European countries.